Tip
This section contains the information on the archive setup on server.
We also recommend that you review the following sections: Archive and Selecting the number of disks for an archive.
In the window Settings -> Archive tab, you can determine which disks and what mode will be used for the archive.
At the top of the window is archive general settings. Below is the list of the drives used by the system (including networks drives, external hard drives, flash-drives, etc.), their statistics and settings.
-
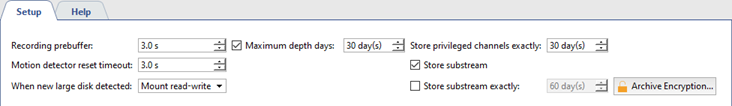
Recording Prebuffer is the size of the video buffer in seconds (from 0 to 10 seconds). A buffer of the indicated size will always be stored in memory. When an event occurs, the buffer is appended to the associated video. This lets the operator later review the archived video not from the moment the event was recorded, i.e. a door opens, but rather several seconds beforehand, making it possible to see who approached the door and how.
-
Motion detector timeout - The amount of time for which motion will be considered to continue after a detector has indicated that motion within the frame has ceased. This parameter makes it possible to avoid cutting off a recording immediately after motion has ceased and continue to record several seconds at the end (from 0 to 10 seconds).
-
When New Large Disk Detected. This parameter determines how the software will respond to a new disk being detected (for example, when a new network drive or a flash drive is connected). There are three possible values:
- Ignore - The disk will be shown in the list, but it will be otherwise ignored by the system; the disk can only be included manually.
- Mount as read-only. Nothing will be recorded to the disk, but if it contains the archive files, they will be available as lost channels.
- Mount as read-write. When a new disk appears in the system, TRASSIR will automatically use it for archive recording.
TRASSIR supports recording of two video streams coming from devices: the main stream and the additional stream (substream). Since the additional stream is generally several times smaller than the main stream, recording it substantially increases the archive depth without changing the required disk space. Moreover, using the sub stream significantly lowers network bandwidth requirements when viewing archived data from several channels simultaneously over a client-server connection.
If necessary, you can mark one or more channels as privileged and assign them an arbitrary archive depth in the main (primary) stream.
- Maximum depth days allows you to set the archive depth for all channels.
- Store Privileged Channels Exactly - Supports assigning a desired archive depth to specific channels.
- Store Substream - Enables recording of the auxiliary stream.
- Save substream Exactly - Supports assigning a desired archive depth to substreams. If no depth is assigned, then the substream will be erased together with the primary stream.
Tip
Be careful when setting up archive depth values. It is possible that, due to an attempt to maintain the desired archive depth of a substream and/or privileged channels, there will not be space under the usual archive. If during the overwriting process the archive depth of the primary stream is less than 24 hours, then the system will issue a warning about incorrect settings for archive recording.
If the flag Store substream exactly is not enabled, the sub-stream archive depth is equal to the greatest depth of the main or privileged stream. The sub-stream archive will contain video from the channels of the devices on which the sub-stream recording is enabled (see Configuring device settings).
You can use encryption of video recordings in order to prevent unauthorized access to an archive. To configure encryption, click Archive encryption....
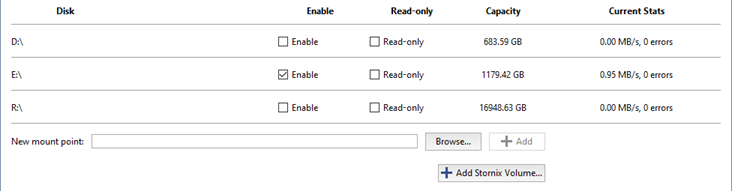
You can set specific settings for each drive:
- Enable - Enables or disables use of the disk in the system.
- Read-only - Enables or disables use of the disk for reading.
- The Capacity column displays the full capacity of the disk (partition).
- The Current Stats column displays the archive's current write speed and the number of errors. Sometimes there may be access errors when attempting to read from or write to a disk. For example, if the connection to a network drive is lost, if a disk cannot handle writing an excessively large stream, or if hardware problems are detected on a disk.
Tip
The "HDD Kicker" script is recommended for local disks. After several errors occur, the script can disable the problematic disk to avoid data loss.
Warning
If a disk's capacity is less than 10 GB, it will be labeled as "Not suitable" in the list. You will not be able to use such a disk for the archive recording. But if it contains the archive files, then it will be displayed in the list and marked as "Read-only".
New mount point - adds any folder for subsequent use of its disk space by the archive. Adding a new mount point may be useful if, for example, you need to view the archive files written to another server that lacks a network connection. You can indicate the folder using the Browse button, or enter the path manually and press Add. No additional steps with the archive are required. Archive data added using a new mount point will be available as lost channels.
Important
Do not merge archive disks of different servers or disks of the same server connected at different time. This may result in the entire archive incorrect operation.
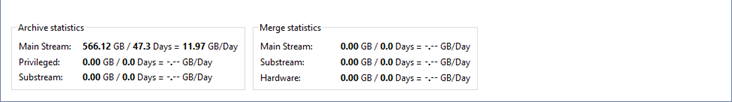
The archive's general statistics are displayed in the bottom part of the window. You can view the depth of days and the total volume of data separately for the primary and auxiliary streams. You can also view the statistics for privileged channels. A calculation of the disk space necessary to store one day of archive recordings is also presented here.
Important
The archive of 4.0 version supports gradual upgrade of the archive from 3.1 version. The entire archive from the older versions will be available as lost channels and will be erased as the new archive is written.
Tip
TRASSIR OS has some differences in the archive settings menu. That is:
- TRASSIR OS does not have a New mount point setting, which means you won't be able to mount an arbitrary folder to the archive;
- you can run Format command from the context menu, which will delete old records of the archive or prepare a new drive for the archive record;
- there is a Store database on setting, which lets you select the disk to store the database on. The selected disk in the list of archive disks will be marked with ('*').